By: Mr. Ombeni Mkamba
A BALANCE DIET
A balanced diet refers to food containing all types of food nutrients in the correct proportion. We should eat a diet low in fats, sugar and salt but high in proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and roughage, more importantly we should take in large amounts of water.
However, it is recommended that we
eat more fish, poultry products and legumes (such as pea, beans and peanuts)
Instead of taking red meat as protein sources. The following should be done in order to maintain a healthy body.
1. Physical activity can preserve
and improve your health. Therefore, it is important to balance your food intake
and exercise.
2. Minimize your intake of fats and
oils by eating foods low in fats, sugars and salts. This will reduce your risk
of heart attacks, tooth decay and high blood pressure respectively.
3. Include plenty of grains, fruits,
and vegetables in your diet.
4. Eating a variety of food will provide the body with energy and nutrients that is required in maintaining proper health.
Nutritional requirements for
different groups of people
Nutritional requirement differ for
different groups of people. The ratio of nutrients varies depending state of
the body. The following are some groups of people and the special nutritional
needs.
1. Expectant and lactating mothers.
Expectant and lactating (breast
feeding) mother need to get enough nutrients.
They should thus eat a
balanced diet because they require nutrients for themselves and the growing
foetus or babies.
Protein is needed for the build – up
of the mother muscles, breast, uterus, blood supply and the baby or foetus
tissue and organs.
Folic acid and vitamin B help to
lower the risk of birth defects such as spina bifida. Spina bifida is a
spinal disorder characterized by a hole in the spine.
It results from incomplete formation
of the spinal cord and the bones of spine. Often the spine protrudes through
the hole and sometimes a fluid filled sac may surround the protruding spinal
cord.
Calcium helps in the development of
the foetus or baby’s bones, if the mothers’ diet does not contain adequate
calcium; it is derived from her bones for the foetus or baby. This weakens the
mother bones.
Zinc is important for the proper
progression of labour and proper growth and development of the baby.
The mother to be requires iron for
her blood supply need, the foetus also needs to store iron for use during the
first few months after birth.
Expectant mother requires adequate amounts of dietary fiber to reduce the
likelihood constipation, which is a common complaints during pregnancy.
2. Children
Children require enough proteins for
the growth and development of body tissues. Inadequate of proteins can lead to
stunted growth.
Minerals like calcium are necessary for the formation of strong bones and teeth. Zinc is important for body growth. The zinc resources in the body can be depleted by vigorous physical exercise.
Vitamin B12 is required
for the formation of red blood cells. Because a growing baby needs more oxygen
and more blood) for growth while vitamin C helps children to build their
immunity.
Children also require more energy –
giving foods because they are active than adult.
3. Adolescent
- Need food rich in carbohydrates because of high body
metabolism
- Food rich in protein and mineral salt such as calcium,
iron and phosphorus
- Adolescent girl require additional supply of iron to
compensate for the blood loss during menstruation.
4.The
elderly.
Elderly people require less energy –
giving foods because they are generally less active than young people. This
group should eat food that is rich in fiber in order to reduce constipation and
bowel problems that come with age.
They also need minerals such
as iron, zinc and calcium. Iron is necessary because anemia is a frequent
problem in older age; zinc is required for a healthy immune system and to
increase the rate of healing of wounds.
Old age comes with the loss of
calcium from bones leading to soft and weak bones that can break easily. Old
people therefore require adequate amounts of calcium and vitamin D to counter
the loss.
The elder often have problems of
chewing tough foods because of weakened teeth and swallowing because of
the decreased production of saliva. It is therefore important to ensure they
get food that are nutritious as well as easy to chew and swallow. For example
they can get proteins from eggs or liver instead of meat.
5. Sedentary workers
These are individuals who stay in
one place for a long time while performing their daily occupational activities.
They include workers potter’s weavers, clerk, receptionists and doctors.
Sedentary workers are encouraged to
balance their diets with physical exercise. Due to their lifestyle and
occupation obesity increasingly is common among them. Therefore, it is
recommended that they limit their intake of foods rich in lipids.
6. The sick
Sick people require plenty for
nutrients to help recover their health, those who have incurable disease such
as HIV and AIDS should get food that will help them to manage their conditions.
Proper nutrition helps to keep their
immune system strong and helps the body to fight opportunistic infections and
disease.
Rapid weight loss is a major problem
in the late stage of AIDS. It is therefore important to get enough nutrients so
as that the body can compensate for this.
Proper nutrition helps the body to
withstand heavy medication.
Proper diet and exercise helps to
combat symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, diarrhea and high blood sugar.
Excess caffeine sugar, dried foods,
spicy foods and alcohol should be avoided because they are harmful to a body
whose immune system is already weak.
They need to take plenty of fruits
and water. Fruits provide vitamins which are required to fight disease. Water
replaces the amount lost through diarrhea or vomiting.
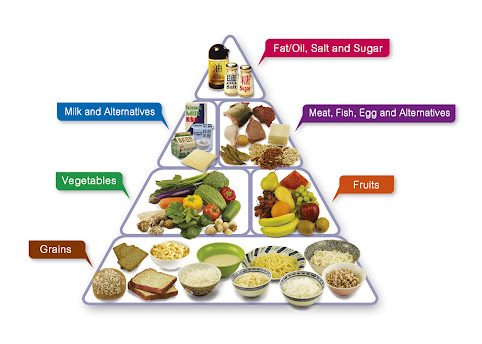
It is advisable to use food guide
pyramid to know what to eat. The food guide pyramid is a chart showing the
recommended amounts of different food types that dietician considers healthy
eating.
Nutritional deficiencies and disorders
Malnutrition
Malnutrition (limiting the intake of
one or more essential nutrients) results from eating too little from eating the
wrong food. There are different types of nutritional deficiencies and disorders
in human beings, these deficiencies and disorders include obesity, rickets,
kwashiorkor, marasmus, anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa.
Nutritional disorders
Nutritional disorders are conditions
of ill health in a person which arise as a result of lifestyle (poor eating
habits) as discussed below.
- Obesity
Obesity is where by a person has
excess body fat. A person sex, age and level of activity among other factor
determine his or her ideal body fat. To maintain fertility, women need more
body fat. Women also store more fat in their breasts, hips and thighs.
Another important influence of body
fat is a person frame size. Individuals with larger bones carry more fat.
Obesity mostly results from eating
too much and not exercising enough. Body weight and health risks associated
with it are correlated by the body mass index (BMI). BMI gives the relationship
between the estimated body fat and the risks of certain disease or conditions.
BMI = Body mass (in kilograms)
persons height (in meters)2
OR
BMI = Body mass (kg).
(Person's height)2 (m2).
For example if your height is 1.65 meters and your body mass is 60 kilograms
your BMI can be calculated as
60/ (1.65)2 = 60/
(2.7225) = 22.04
If an individual’s BMI falls in the
range of 20 – 25, this is considered to be healthy. On the other hand if the
BMI is over 30, one may be at risk of diseases associated with obesity.
The following table shows a general
guide of how different values of BMI are used to define the condition of the
body.
Table BMI
guide
|
BMI |
Body condition |
|
Below 20 |
Underweight |
|
20 – 25 |
Advisable range |
|
25 – 30 |
Overweight |
|
30 – 35 |
Obese |
|
Above 35 |
Very obese |
Obesity increases the like hood of
conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes and certain types of cancer,
stroke, and respiratory problems.
Obesity can be prevented by eating
properly and engage in regular exercise. The intake of calories should balance
one’s physical activity. It is also important to avoid eating too much fat
foods such as butter, fat meat, chips, margarine, sausage and vitumbua. Avoid
also unhealthy dieting.
Anorexia nervosa and Bulimia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa is also called slimmer’s disease or self starvation
syndrome. It occurs when a person intentionally refuses to eat enough, leading
to a severe loss of body mass.
Sign and symptoms of anorexia
1. Muscle wasting (including
weakening of heart muscle)
2. Excessive loss of body mass
3. Extreme fear of being fat.
4. Disturbed body image or feeling
fat even when one is very thin.
Bulimia nervosa involves excessive eating followed by efforts to remove
food from the body. This effort could involve self- induced vomiting, fasting,
excessive exercising or taking drugs that stimulate, emptying of the bowels or
excessive urination. Bulimics usually have a normal body mass and keeps their
eating behavior secret. Hence it may be difficult to tell that they have a
problem.
Causes of Anorexia and Bulimia
Both Bulimia and Anorexia have
underlined psychological causes, such as depression, low self esteem and
bottled up emotions and the need to fit contemporary standard of beauty Bulimia
and Anorexia mostly affect women.
Effects of Anorexia and Bulimia
- The effects of Anorexia and Bulimia are demonstrated by
heart problems due to weak cardiac muscles or an imbalance of mineral
salts.
- There is an impaired mental function because the brain
lacks adequate amount of glucose. Victims also exhibit dehydration. During
vomiting, the acidic present in the stomach come into contact with the
teeth and gums, the eventually causes, serious damage to the gum and
erosion of the teeth. Other effects include anemia, stomach ulcers,
abdominal cramping and inflammation of the gut, irregular or absent
menstrual periods and dry skin.
Treatment for Anorexia and Bulimia
Anorexia and Bulimia can be treated
by resolving the underlying psychological problems, seeing a medical
practitioner who can prescribe a way of getting back one’s healthy and making
the necessary lifestyle and dietary change.
Nutritional deficiencies.
These deficiencies arise when the
body does not have sufficient supply of a particular food or nutrient. The
following are some of the common nutritional deficiencies.
- Marasmus
Marasmus is a form of malnutrition
in children caused by lack of adequate amount of food
Sign and symptoms of Marasmus
A child suffering from marasmus
shows weight loss, slowed growth, decreased activity and lack of energy. They
also have wrinkled skin, are irritable and have extreme hunger
Treatment of Marasmus
Getting adequate amount of food that
contains all the nutrients in the right proportions.
2. Kwashiorkor
Kwashiorkor is caused by a
deficiency of proteins. It affects children, mostly after stopping to breast
feed.
Signs and symptoms of kwashiorkor
The signs and symptoms of
kwashiorkor include extremely thin arms and legs, poor growth, swollen thin
arms and legs, swollen abdomen due to enlargement of the liver and reddish or
yellowish thin and weak hair. Other symptoms are weakened immunity, diarrhea,
anemia, and dry skin that cracks easily
Treatment for kwashiorkor
Kwashiorkor is treated by providing
a child with a diet that has adequate amounts of proteins.
3. Rickets
Rickets is a condition where by the
bones of a child soften, leading to fractures and deformities. The cause of
rickets is lack of vitamin D, phosphorous and calcium.
Sign and symptoms of Rickets
A child suffering from rickets can
be identified by observable skeletal deformities such as bow legs, knock knees,
an odd – shaped skull and a deformed spine. A child feels bone pain,
experiences dental problems such as weak teeth or delayed formation of teeth
and develops weak muscles. The child’s bones are easily fractured, shows slow
growth and gets muscle spasms and muscle cramps.
Prevention of Rickets
Rickets is prevented by increasing
the amount of vitamin D, phosphates and calcium in the diet and by ensuring
exposure to sufficient amount of sunlight.

0 Post a Comment:
Post a Comment